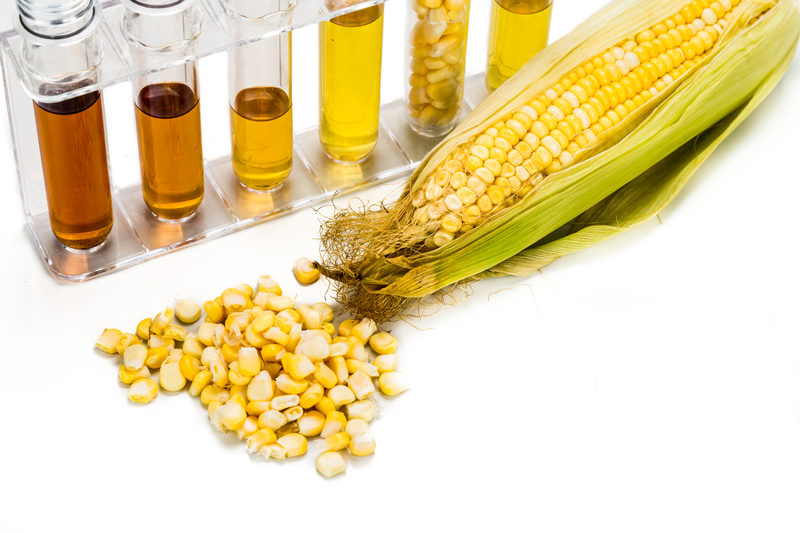
This article is your guide to understanding what biofuel energy is. Are you curious about renewable energy options for your home? Many consumers are looking for alternative ways to power their homes with the rising costs of electricity bills. That is where biofuels come in, which are a type of green energy derived from plants, crops, and waste materials. Biofuels can be used to power your car or your home, depending on the type of organic fuel you choose to use!
In this article, we are going to cover the world of biofuels explaining what they are, how they’re formed, and the best ways to use them in your life. So, if you’re looking to reduce your carbon footprint, or looking for ways to lower your electricity bill, you’ll want to learn more about biofuels 2024.
Here at The Energy Professor, we want to give you the information you need to not only save money on your energy bill but to also become more energy efficient. We hope find this post helpful! And makes it easier for you to know more about appliance energy usage. Be sure to also check out our one-of-a-kind energy savings calculator!
The Energy Professor Electricity Rate Check Tool
What is Biofuel Energy?

Biofuel is a liquid fuel type derived from biomass, which is living materials such as plants and animal waste. These fuel products from plants and animals are a class of renewable energy, as they are considered an alternative to fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. Biofuels are mainly used for transportation, but can also be used for heating systems and electricity generation.
There are also different types of biofuel which are categorized based on generation and their production process. The first-generation biofuels come from plants like corn, sugarcane, and vegetable oils. Second-generation biofuels come from non-edible plants, such as plant waste and leftover crops (stalks of wheat, corn, and wood). Third-generation biofuels are considered advanced bioenergy and are often called “algae fuel” as they are derived from algae and microorganisms.
How are biofuels made?
In short, biofuels are made from the transformation of plants, crops, or waste materials. The most common way they’re produced is through biomass fermentation. Since there are different types of biofuels, there are varying ways to produce these renewable types of energy, which we will briefly cover. Biodiesel is created by mixing either vegetable oils or animal fats with alcohol to create a chemical reaction that converts it into biodiesel. Bioethanol is made by fermenting sugars and starches to produce ethanol which will then be refined.
Why are biofuels important?
Biofuel energy is important for a few key reasons. First, they’re renewable, which means we can continue to produce them without running out, unlike fossil fuels. When we burn biofuels, they also release less harmful greenhouse gasses compared to fossil fuels, which can help combat climate change. On top of that, biofuels can boost our energy security by reducing our reliance on imported fossil fuels, creating job opportunities in agriculture and biofuel industries, and driving technological innovation for a greener future. So, they’re a pretty cool and important part of the renewable energy mix!
What are the different types of biofuel?
In this section, we will cover all three generations of biofuel and examples of biofuel in each category.
- First-generation – Food-based crop biofuels
- Biodiesel: Derived from vegetable oils or animal fats.
- Bioethanol: Produced through the fermentation of sugars and starches found in crops like corn or sugarcane.
- Second-generation – Non-edible plant-based biofuels
- Cellulosic ethanol: Made from non-edible plant materials, such as agricultural residues, wood chips, or grasses.
- Renewable diesel: Produced from various feedstocks, including vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste fats.
- Third-generation – “Algae fuel”
- Algae-based biofuels: Derived from the oils produced by algae, which can be grown in various water sources.
- Synthetic biofuels: Created through chemical reactions using biomass or other renewable resources.
Each generation of biofuels represents advancements in technology and feedstock selection, with a focus on improving sustainability and reducing environmental impacts.
Related post: What is Green Energy?
How is Biofuel Produced?

Since there are many different varieties of biofuel types, there are several processes to produce them. As we discussed above, each generation of biofuel is produced from either edible plant material, non-edible plant material, or algae, which means they all need to be processed differently. Therefore, we are going to cover a simplified overview of how biofuels are produced for each generation.
First-generation biofuel production:
- Biodiesel: Vegetable oils or animal fats are mixed with alcohol and a catalyst, which undergoes a chemical reaction called transesterification. This process converts the oils/fats into biodiesel, which is then separated and refined.
- Bioethanol: Crops like corn or sugarcane are harvested and processed to extract sugars. These sugars are then fermented using yeast or other microorganisms, which convert them into ethanol. The ethanol is separated and refined for use as biofuel.
Second-generation biofuel production:
- Cellulosic ethanol: Non-edible plant materials like agricultural residues, wood chips, or grasses are treated with chemicals or enzymes to break down the complex carbohydrates into simple sugars. These sugars are then fermented and distilled to produce ethanol.
- Renewable diesel: Various feedstocks, including vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste fats, are subjected to a refining process called hydrotreatment. This process removes impurities and converts the feedstocks into renewable diesel fuel.
Third-generation biofuel production:
- Algae-based biofuels: Algae, which can grow in water sources, are cultivated and harvested. The oils produced by the algae are extracted and processed to obtain biofuels, such as biodiesel or bioethanol.
- Biomass or other renewable resources are chemically transformed using different processes, such as gasification or catalytic conversion. These processes convert the biomass into synthetic biofuels that can be used as alternatives to conventional fuels.
How can I use biofuels in my home or day-to-day life?
There are several reasons for biofuel use in your day-to-day life such as heating, transportation, or even cooking! If you have a heating system that runs on oil or propane, there could be a biofuel alternative available instead. Biofuels such as biodiesel can be blended with other traditional heating oils to heat your home. Biodiesel can also be used to power a diesel-powered vehicle with compatible blends of biodiesel such as B20. If you’re grilling out, you can even use bioethanol for certain portable stoves which offer a clean-burning alternative to charcoal or wood.
Related post: Why is Energy Conservation Important?
What are the Pros and Cons of Biofuel Energy 2024?

While it seems like biofuel energy could be an incredible solution to the depletion of fossil fuels, there are many things you should consider. Biofuels don’t come without a cost, and they are not only expensive but also pose the same problems of deforestation as we need space to grow them. So with that being said, we are going to cover the pros and cons of biofuels in 2024.
Pros of biofuels
- Renewable and sustainable: Biofuels will reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and can be replenished through sustainable agricultural practices. Biofuels will also significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions because the plants used to create the biofuels also absorb carbon dioxide. This can help mitigate the effects of burning fuels.
- Energy security: When you don’t have to rely on imported fossil fuels, it increases energy independence. That means there could be more reliable price fluctuations, unlike in the gas and oil markets.
- Job creation: Biomass production opens the door for brand new opportunities for farmers and agricultural communities.
Cons of biofuels
- Land use: Producing biofuels requires a lot of land, which can lead to deforestation or the destruction of natural habitats. This could also lead to soil degradation, increased water usage, or other negative environmental impacts.
- Expensive to produce: Currently, biofuels are rather expensive to produce, but with technology advancing consumers won’t have to invest as much to use them.
- Limited energy density: While biofuels seem like a great alternative to fossil fuels, they don’t have as much energy density as conventional. That means you need a lot more biofuel to achieve the same goal as a fossil fuel.
Related post: How Does Geothermal Energy Work?
Biofuel Energy FAQ
Q: What is biofuel in simple terms?
A: Biofuel is a type of fuel derived from living materials like plants and animal waste. Biofuels are considered a renewable energy source because they can be produced over and over without depleting themselves. Biofuels are an alternative to non-renewable resources such as coal, oil, and natural gas. Biofuels are typically used for transportation, but can also be used for heating systems and electricity generation.
Q: What is an example of biofuel?
A: One example of biofuel is biodiesel, which is made from vegetable oils or animal fats. Another example is bioethanol, which is produced by fermenting sugars and starches found in crops like corn or sugarcane. These biofuels can be blended with or used as alternatives to traditional fuels.
Q: What are 5 examples of biofuels?
A: Here are five examples of biofuels:
- Biodiesel: Made from vegetable oils or animal fats.
- Bioethanol: Produced through the fermentation of sugars and starches found in crops like corn or sugarcane.
- Cellulosic ethanol: Derived from non-edible plant materials such as agricultural residues, wood chips, or grasses.
- Renewable diesel: Made from various feedstocks, including vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste fats.
- Algae-based biofuels: Derived from oils produced by algae, which can be grown in water sources.
Q: What are biofuels and what do they do?
A: Biofuels are fuels produced from organic matter, such as plants and animal waste. They offer an alternative to conventional fossil fuels and can be used for various purposes. Biofuels are mainly used in transportation, where they can be replaced or blended with gasoline or diesel fuels. They can also be used in heating systems, electricity generation, and even for cooking and grilling.
Q: What is biodiesel made out of?
A: Biodiesel is made from vegetable oils, such as soybean oil, canola oil, or used cooking oil, as well as animal fats. These feedstocks are mixed with alcohol, usually methanol or ethanol, and a catalyst. The mixture undergoes a chemical reaction called transesterification, which converts the oils or fats into biodiesel. The resulting biodiesel can be used as a cleaner-burning alternative to petroleum-based diesel fuel.
Do you Need Cheaper Electricity?
If you’ve taken the time to understand the information on your bill and discovered you’re paying more than you’d like for your electricity, have you looked around for a cheaper deal? The Energy Professor has a wealth of information on ways to save on your utilities, including details of top deals that could significantly reduce your monthly or quarterly electricity bills.
We hope you found this article helpful! If you are looking for ways to increase energy efficiency and sustainability in your home be sure to look at the latest renewable energy options in your area. The Energy Professor helps residential and small business owners find qualified energy suppliers in New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Texas, Ohio, Maryland, Illinois, and Massachusetts


